Innovative Approaches to Enhance Patient Safety
Patient safety is a key issue in health care. It is closely tied to the quality of health care and patient health outcomes. Despite significant advancements in medical science, healthcare providers worldwide still struggle to ensure and enhance patient safety. To address this challenge, innovative approaches are being developed to enhance safety and prevent harm to patients. These methods involve using advanced technology, improving communication among healthcare teams, and creating safer care environments. This guide explores new strategies and technologies to enhance patient safety, reducing medical errors, enhancing care quality, and ultimately saving lives.
Understanding Patient Safety
Understanding patient safety is crucial for improving health outcomes and building trust in the healthcare system. Patient safety involves protecting patients from harm during healthcare by reducing risks, errors, and injuries.
Definition and Importance of Patient Safety
Patient safety means protecting patients from harm during healthcare. It is a critical dimension of healthcare quality. Patient safety seeks to prevent or eliminate adverse outcomes or injuries stemming from healthcare delivery. Patient safety is not just about avoiding mistakes and preventing errors but also about building systems and processes that prevent harm.
Current Challenges in Patient Safety
Despite ongoing improvements, challenges like medication errors, hospital-acquired infections, surgical complications, and diagnostic errors persist. Medication errors alone affect millions of patients worldwide each year. Addressing these challenges requires fresh thinking and innovation, and the entire healthcare community must work together to find solutions.
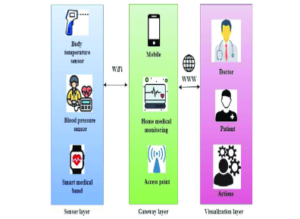
Technological Innovations
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) is one of the most significant advancements in medical technology. EHRs enhance patient safety by ensuring that patient records are accurate, up-to-date, and complete at the point of care. They help reduce medical errors caused by illegible handwriting and make medication management and communication among healthcare providers more efficient. Since adopting EHRs, medical errors have significantly decreased, leading to much better patient outcomes.

Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) are another key innovation in healthcare. CDSS assists healthcare providers by offering evidence-based recommendations and helping with clinical decisions. For example, CDSS can alert doctors to dangerous drug interactions, suggest diagnostic tests, or recommend treatment strategies based on evidence and patient data. By providing these suggestions in real-time, CDSS can enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve the quality of care.
Barcoding and RFID Technology
Barcoding and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies have greatly improved patient safety. These tools ensure that the right patient receives the right medication at the right time and in the correct dose. Enhancing tracking, barcoding, and RFID tags helps reduce the risk of medication errors that could endanger patient safety.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine allows doctors to provide care to patients from a distance using video calls, phone calls, or online messaging. Remote monitoring uses devices to track a patient’s health, like heart rate or blood pressure, even when they are not in the hospital. Together, these technologies enhance patient safety by allowing doctors to check on patients regularly, catch problems early, and give timely advice without needing the patient to visit the hospital.
Process Innovations
Standardized Protocols and Checklists
Standardized protocols and checklists are simple yet effective tools to enhance patient safety. They ensure that everyone follows the same procedures and that all necessary steps are completed during treatment, reducing variations in care. For instance, surgical checklists help ensure that every required step is followed, leading to fewer postoperative complications and lower mortality rates. Similarly, standardized treatment protocols increase consistency in care, resulting in better patient outcomes.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
If you can figure out what went wrong, it can help prevent it from occurring again. The Root Cause Analysis (RCA) process is systematic and provides an analysis of the underlying causes of a safety incident. By diagnosing why an error happened, medical teams can prevent the problem from recurring by addressing the root causes. RCA can be lengthy and complex, involving thorough investigation and analysis of the event and its contributing factors. This process helps uncover systemic issues and improves safety within the healthcare setting.
Just Culture and Safety Culture
Healthcare organizations primarily promote a Just Culture and a Safety Culture. A Just Culture encourages learning from mistakes by not punishing them, which leads to better safety and quality in the future. A Safety Culture makes safety a core value and an essential part of healthcare delivery.
Simulation Training
Simulation training enhances patient safety by allowing healthcare staff to practice and refine their skills in a controlled environment. By creating realistic scenarios, staff can prepare for emergencies, test their responses to critical events, and improve their decision-making abilities. This hands-on practice boosts their competence and confidence, leading to better handling of real-life situations and ultimately enhance patient safety.
Patient Engagement and Education
Empowering Patients
Patient empowerment can also enhance patient safety. When patients are informed and actively involved in their care, they are more likely to follow treatment plans, report adverse events, and take preventive measures. Providing tools and resources that help patients understand their treatment plans and medications can significantly improve safety outcomes.
Patient Education Programs
Another effective strategy is to develop educational programs that teach patients about safety practices like medication management, infection prevention, and warning signs of complications. When patients are well-informed, they can better manage their health and collaborate with healthcare providers on safety.
Feedback Mechanisms
Setting up systems for patients to provide feedback on their care experience is essential. Feedback reveals what works well and highlights areas needing improvement. By using this data to make informed changes, providers can enhance patient safety overall.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Role of Data Analytics
Large data sets can reveal patterns that contribute to patient safety incidents. Analytics help service managers identify risks and target areas for intervention. These patterns also inform future safety measures. For example, data-driven insights can guide changes aimed at improving care delivery.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling enhances patient safety by using data to anticipate potential risks before they occur. By analyzing patterns and trends from past data, predictive models can identify patients at higher risk for complications or errors. This allows healthcare providers to take preventive measures, design care plans, and address potential issues early, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing safety incidents.
Collaborative Approaches
Interdisciplinary Teams
Another strategy to enhance patient safety is forming interdisciplinary teams of physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals. These teams can develop comprehensive solutions to patient safety issues by drawing on the unique knowledge and experiences of each member.
Partnerships and Networks
Partnerships and networks enhance patient safety by enabling healthcare organizations to share best practices, resources, and knowledge. Through collaboration, these groups can learn from each other’s successes, address common challenges, and continuously improve care quality. By working together, they create a stronger, more unified approach to ensuring patient safety.
Conclusion
Patient safety is a complex and multifaceted goal that requires technological innovations, process improvements, patient engagement, data analytics, and collaboration. Innovation is essential to reduce errors, improve care, and save lives. This need for continuous innovation and improvement is another argument for patient safety being at the heart of healthcare delivery and the systems that underpin it: we must continually work on patient safety and invest in it to improve the quality of health outcomes and build a more reliable healthcare system tomorrow.

