
The Role of Telehealth in Enhancing Patient Safety and Care Access
Telehealth is revolutionizing healthcare by improving patient safety and expanding access to care. It uses digital platforms for remote consultations, real-time monitoring, and efficient management of health conditions. This is especially beneficial for those in underserved or remote areas. By bridging gaps in accessibility and facilitating timely medical interventions, telehealth enhances the quality of care. It ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate treatment. This makes telehealth a crucial component in modernizing and improving healthcare delivery.
Understanding Telehealth
Overview of Telehealth
Definition and Components of Telehealth
Telehealth uses digital technologies to provide and manage healthcare services remotely. It enhances access to care and improves patient outcomes. Key components include telemedicine for virtual consultations and remote diagnoses. Teleconsultation allows specialists to collaborate on patient care. Remote patient monitoring tracks health data and transmits it to healthcare providers. Teletherapy offers mental health support through digital platforms. Health information technology ensures secure data sharing among providers. Mobile health (mHealth) involves using apps to manage health on the go. Telepharmacy enables remote medication management. Together, these elements streamline healthcare delivery and improve patient care.
Types of Telehealth Services

Telemedicine: Provides remote clinical services through video calls, phone consultations, or online platforms for diagnosing and treating patients. It includes virtual doctor visits and remote consultations with specialists.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Remote patient monitoring uses digital medical devices such as health trackers, smartwatches, and biosensors to collect real-time health data from patients and send it to care providers. This includes continuous recording of patients’ blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, and so on.
Mobile Health Apps: Mobile health (mHealth) is defined by the World Health Organization as ‘medical and public health practice supported by mobile devices, such as mobile phones, patient monitoring devices, personal digital assistants and other wireless devices’. However, it is perhaps best described as a health-related purpose-built application for smartphones and tablets that helps the user manage his or her health and wellness. mHealth apps can help a user monitor his or her medications through dosing reminders, track his or her physical activity and fitness, and receive care through telemedicine.
Teleconsultation: Facilitates real-time consultations between healthcare professionals, such as primary care physicians and specialists, to discuss patient cases and make collaborative decisions.
Teletherapy: Offers mental health services, including therapy and counseling, through video calls or chat-based platforms, providing support for emotional and psychological well-being.
Telepharmacy: Provides medication management services remotely, allowing pharmacists to consult with patients about their prescriptions, check for interactions, and support adherence.
Tele-ICU: Monitors and manages intensive care unit (ICU) patients remotely using advanced technologies and expert consultations to support critical care.
Telehealth Education: Delivers health education and training remotely for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals, including workshops, seminars, and informational sessions.
Historical Development of Telehealth
Evolution from Early Telemedicine to Modern Telehealth Solutions
Telemedicine began in the early 20th century with ship captains using radio to transmit basic medical advice, like sending a blood pressure cuff and suggesting, “Take two aspirin and call me in the morning.” Over time, the term “telemedicine” has come to refer to specific telehealth solutions in some countries. By the latter half of the 20th century, advancements in communication networks, such as telephone landlines, new computer networks, and affordable mobile technology, showed that delivering quality patient care no longer relied solely on being physically present at the bedside.
Key Milestones and Technological Advancements
1960s: Closed-circuit television links are used for psychiatric consultations in the first telemedicine projects.
1965: The first phone consultation occurs.
1967: The first captured still image transmitted through space is viewed via television.
1990s: The rise of internet transmission expanded telemedicine’s reach significantly. Now, medical data and virtual consultations can be conducted from virtually anywhere.
2000s: Mobile technology and smartphones introduced mobile health applications, making telehealth a standard part of healthcare.
2020s: The COVID-19 pandemic led to greater acceptance of telehealth as regulatory laws changed and investments in telehealth infrastructure increased. These changes highlighted the importance of telehealth in maintaining a continuous system of care.
Enhancing Patient Safety with Telehealth
Reducing Exposure to Infectious Diseases
Minimizing In-Person Visits
Telehealth offers a significant advantage by reducing the need for in-person visits. It reduces the risk of exposure to infectious diseases for both patients and healthcare providers. Patients can consult doctors remotely from the safety of their homes, avoiding potentially crowded clinics. This is especially beneficial for those with chronic illnesses, as well as elderly and immunocompromised patients.
Benefits During Pandemics (e.g., COVID-19)
The COVID-19 outbreak highlighted the crucial role of telehealth in maintaining healthcare delivery while minimizing in-person encounters that could spread the virus. Telehealth helps sustain continuous care for patients and supports public health efforts to screen and monitor the spread of the coronavirus. It also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities by lowering non-emergency in-person visits.
Improving Medication Management
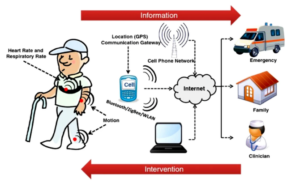
Remote Prescription Monitoring
Remote prescription monitoring lets doctors and pharmacists track a patient’s medication use without in-person visits. They use digital tools to see if patients take their medications correctly. They can also check for drug interactions and adjust prescriptions as needed. This helps keep patients on the right treatment plan and reduces the chance of mistakes. It also makes managing health from home easier for patients.
Telepharmacy Services
Telepharmacy services allow pharmacists to manage medications and provide advice through remote consultations. These services include professional guidance on medication use, virtual consultations for complex medication regimens, and timely support for any medication-related concerns.
Enhancing Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
Remote patient monitoring devices help doctors track a patient’s health from a distance. These devices collect data like heart rate, blood pressure, or glucose levels and send it to healthcare providers. Doctors can then see how the patient is doing without needing an in-person visit. This helps catch any issues early and keeps patients on the right treatment plan, all from the comfort of their own homes.
Continuous Health Tracking and Early Intervention
Telehealth platforms enable continuous health tracking, which serves as a form of preventive care by identifying early signs of health problems, even when symptoms are absent. With timely intervention, doctors can manage the disease and potentially stop its progression. This approach reduces hospital readmissions and improves patient outcomes.
Facilitating Access to Specialists
Virtual Consultations with Specialists
Geographical barriers often prevent people from accessing specialist medical care. Telehealth now removes these barriers by allowing patients to have virtual consultations with specialists from anywhere in the world. As a result, more people can benefit from the convenience of a virtual second opinion without needing to travel long distances. This increased access to specialized care leads to better diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
Reducing Wait Times and Improving Outcomes
Telehealth platforms reduce wait times for specialist appointments, which is especially helpful for conditions that benefit from early treatment. This increased convenience in accessing healthcare services leads to better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
Expanding Care Access with Telehealth
Reaching Rural and Underserved Areas
Overcoming Geographical Barriers
Telehealth removes barriers and helps people in rural and underserved areas access care. Patients can connect with healthcare providers over long distances. For example, if a telehealth provider is in one city and the patient is in another, telehealth allows them to connect virtually, eliminating the need for the patient to travel to an urban center. This makes it easier for those in remote areas to receive the care they need.
Providing Care to Remote Populations
Telehealth extends healthcare services to underserved populations, including both rural communities and underserved urban areas with limited access to facilities. This approach ensures that all patients, regardless of location, have access to quality healthcare.
Increasing Accessibility for Mobility-Impaired Patients
Home-Based Consultations
For patients suffering from mobility limitations, telehealth provides an easy and accessible option to connect with medical services. It removes the need to travel and helps to keep patients connected to medical care through home-based consultations. Ultimately, this improves their welfare and encourages them to be more involved in their healthcare management.
Reducing Transportation Challenges
The absence of on-site mobility removes transport-related barriers. It is beneficial for elderly patients, those with physical disabilities, and others who find it difficult to travel to healthcare facilities. By bringing healthcare directly to patients’ homes, telehealth improves access and reduces the burden on both patients and their families.

Supporting Mental Health Services
Teletherapy and Counseling
One of the most significant advances in telehealth is the expansion of mental health services through teletherapy and remote counseling. Patients can now access therapy and counseling from licensed providers in the privacy of their own homes. This development has reduced the stigma associated with seeking mental health care and significantly increased the availability of essential mental health services.
Expanding Access to Mental Health Professionals
Telehealth shortens the distance between patients and providers but doesn’t eliminate it entirely. Updated telehealth services can connect patients with distant mental health professionals, allowing them to access a wider range of providers such as psychiatrists, psychologists, and counselors. This is especially beneficial for those living in areas without local mental health services, helping them receive timely and appropriate care.
Providing Continuous Care

Chronic Disease Management
Telehealth plays a crucial role in managing chronic diseases. For instance, people with long-term health issues like diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease benefit from regular check-ins and follow-ups through telemedicine. Patients can stay in touch with their doctors, monitor their health metrics, and receive timely interventions, all through telehealth services.
Post-operative and Follow-Up Care
Telemedicine is crucial for post-operative care, allowing patients to have follow-ups and periodic medical examinations without visiting the doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital in person. By avoiding the need for patients to travel for minor checks and wound monitoring, telemedicine greatly reduces the risk of complications after surgery. Patients can also communicate with their doctors, receiving support for any issues they encounter after the operation.
Technological Innovations in Telehealth
Advancements in Telecommunication Technology
High-Speed Internet and Mobile Networks
Recent expansions in high-speed internet and mobile networks have made today’s advancements possible. Fast and reliable connections now enable video consultations and real-time data monitoring between patients and healthcare providers. The next step in improving telehealth is adopting even faster and more stable technology, like the recent rollout of 5G.
Video Conferencing Platforms

Video conferencing platforms play a crucial role in enhancing patient safety and improving access to care in telehealth. They allow patients and healthcare providers to connect remotely, facilitating consultations, follow-ups, and real-time discussions. By enabling virtual visits, these platforms reduce the need for in-person appointments, which helps minimize exposure to infections and other health risks. They also make healthcare more accessible for patients in remote or underserved areas, providing them with timely medical advice and support.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Seamless Data Sharing and Coordination of Care
Integrating telehealth services with electronic health records (EHRs) improves communication and coordination among healthcare providers. During a virtual consultation, providers can access additional clinical data from the EHR, which was originally collected during in-person visits. They can update the patient’s record in real-time and use this information to guide the care plan effectively.
Enhancing Continuity and Accuracy of Patient Records
EHR applications that integrate with new technology ensure a more accurate and complete patient record. By directly entering telehealth visit details into the EHR, these modules provide comprehensive documentation of patient interactions. This integration improves decision-making, continuity of care, and patient outcomes.
Development of Wearable Health Devices
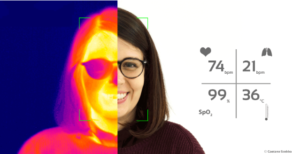
Monitoring Vital Signs and Health Metrics
Wearable health devices are becoming crucial in telehealth. For example, a registered nurse monitors a septuagenarian’s heart rate and other health metrics sent from his smartwatch during the pandemic lockdown. The nurse tracks the patient’s glucose levels, blood pressure, activity levels, heart rate, and weight. They even hold video conferences several times a week to discuss these readings. This data aids in managing chronic conditions and overall patient care. Wearable devices range from smartwatches made by Apple, Garmin, and Fitbit to clinical tools like electrocardiogram devices and glucometers.
Real-Time Data Transmission to Healthcare Providers
Wearable health devices enable real-time data sharing with healthcare providers, allowing them to address health issues and manage a patient’s condition promptly. By monitoring changes in physiological parameters in real time, providers can quickly detect any issues. They can then adjust treatment plans and implement proactive care, which improves the overall level of care. Continuous tracking of health parameters enhances both the safety and quality of patient care.
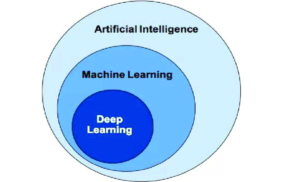
AI and Machine Learning in Telehealth
Predictive Analytics for Patient Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming patient care and management with predictive analytics. By analyzing large datasets, AI and ML can identify patterns and predict future health states. This includes detailed insights into individual patients and broader trends within patient groups. Predictive analytics help establish and monitor management protocols, enhancing patient safety and care quality. For example, AI can determine the optimal time for hospitalization or discharge and predict risks such as psychiatric issues leading to hospitalization or imminent myocardial emergencies. It can also automate radiological imaging to forecast recovery times and predict hospital readmissions, early disease onset, and outcomes. This guidance allows for timely therapeutic interventions before diseases fully develop.
Personalized Care and Decision Support
Machine Learning (ML) enables personalized care by allowing healthcare providers to analyze individual patient data. This analysis helps develop tailored interventions and treatments for each patient. ML also provides decision support by offering options based on medical evidence, recommending potential drug interactions, and suggesting alternative therapies. By designing treatments specifically for each patient’s needs, personalized care improves patient outcomes.
Addressing Challenges in Telehealth Implementation
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy

Compliance with HIPAA and Other Regulations
Compliance with HIPAA and other regulations is crucial in healthcare, particularly in telehealth. HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, sets strict guidelines for protecting patient privacy and securing health information. Telehealth services must follow these regulations to ensure that patient data remains confidential and secure during virtual consultations and when using digital tools. Compliance with HIPAA and similar regulations helps build trust between patients and providers, ensuring that sensitive information is handled with the utmost care and that legal standards are consistently met.

Protecting Patient Information from Cyber Threats
Protecting patient information from cyber threats is crucial in healthcare. As more medical records and consultations go online, they become targets for hackers. To keep this data safe, healthcare providers use strong encryption and secure passwords. They also update their systems regularly and use firewalls and antivirus software to block unauthorized access. Training staff on cybersecurity best practices helps reduce risks. Keeping patient information secure not only meets legal requirements like HIPAA but also maintains patient trust and prevents harmful data breaches.
Overcoming Technological Barriers
Addressing Digital Literacy and Access Issues
Low digital literacy and accessibility challenges can make it difficult for patients and providers to use telehealth services. To address this, healthcare providers are offering instructional and informative resources to guide patients. Training sessions, user guides, and tutorials help improve digital literacy for both patients and providers. Some countries are also tackling accessibility by providing low-cost internet services and affordable devices, making telehealth more accessible to everyone.
Providing Technical Support for Patients and Providers
Technical assistance is essential for the effective use of telehealth. A well-established technical support program must include dedicated services to help patients and providers use the telehealth platform correctly. These support services should also offer expertise in troubleshooting any technical issues that arise. Prompt resolution of these issues ensures that telehealth programs run smoothly without disruptions.
Managing Reimbursement and Insurance Policies
Navigating Telehealth Reimbursement Models
Navigating telehealth reimbursement models can be challenging. These models differ based on location, insurance providers, and the services offered. Healthcare providers need to understand the rules and policies for telehealth payments, including those from Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. Keeping up with changes in reimbursement rules and maintaining accurate documentation are key to receiving fair payment. By managing these models well, providers can offer telehealth services while staying financially sustainable.

Advocating for Policy Changes to Support Telehealth
Supporting the growth of telehealth involves advocating for policy changes that ensure its ongoing success. To safeguard telehealth’s future, we need to lobby policymakers, healthcare organizations, and professional associations for favorable billing and reimbursement regulations. Effective advocacy will help create the pathways necessary for telehealth to thrive in healthcare delivery.
Maintaining Quality of Care
Establishing Telehealth Best Practices
Quality of care in telehealth should be maintained by developing best practices. Standardizing virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and patient education ensures that telehealth is reliably and routinely provided. Best practices should be continually reviewed and updated, considering emerging evidence and technological developments.
Training Healthcare Providers in Virtual Care Delivery
Training healthcare providers in virtual care delivery is crucial for successful telehealth implementation. Providers need to learn how to use telehealth platforms effectively, communicate clearly in virtual settings, and manage patient interactions remotely. Training programs should cover technical skills, best practices for virtual consultations, and how to maintain patient confidentiality. Well-trained providers can deliver high-quality care, enhance patient satisfaction, and ensure that virtual visits are as effective as in-person appointments.
Future Trends in Telehealth
Emerging Technologies in Telehealth

Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Telehealth benefits greatly from Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies, which deliver medical support and therapy as effectively as, or even better than, in-person consultations. VR offers immersive therapy sessions where patients can enter and interact with virtual 3D environments. They can simulate various scenarios, change their virtual body image, or engage in virtual classes like yoga or dancing with AI-simulated assistants. These VR sessions provide a high level of immersion while reducing risks and costs associated with real-life settings. VR also helps with pain relief by allowing users to visualize and control their surroundings, which can reduce perceived discomfort.
AR further enhances pain management in hospitals. Remote doctors can guide nurses through effective pain-relieving treatments, like diathermy, using instructions on their devices and AI assistance. Additionally, AR opens new possibilities for interactive patient education. AR technology can connect patients and hospital staff through data pipelines, offering personalized care and enabling clinicians to tailor content based on each patient’s sensory needs.
Advanced Remote Monitoring Tools
New remote monitoring tools are advancing to enhance telehealth services. These tools include advanced wearables, implantable sensors, and improved home monitoring systems. For instance, they now feature video components that help detect seizures before they occur, going beyond the capabilities of current monitoring tools for managing epilepsy.
Policy and Regulatory Developments
Expected Changes in Telehealth Regulations
Changes in telehealth regulations aim to improve access and quality of care while addressing emerging challenges. Regulators may update policies to expand coverage for telehealth services, streamline reimbursement processes, and ensure privacy and security of patient data. They might also introduce new standards for technology and training to ensure consistent and effective care. As telehealth evolves, regulations will likely adapt to support its growth and address any issues that arise, ultimately enhancing the delivery of healthcare services.
Impact on Telehealth Adoption and Utilization
Simplifying and improving telehealth regulations will likely boost its adoption and integration into broader healthcare services. More healthcare providers will start offering telehealth services, and more patients will gain access to remote care. As a result, telehealth will become a more common part of overall healthcare delivery.
Increasing Integration with Healthcare Systems
Telehealth as a Standard Component of Care
Telehealth is becoming a standard part of care delivery. By integrating telehealth into routine care, healthcare providers can offer a full range of services, both in-person and remotely. This integration improves care coordination, enhances patient outcomes, and supports a more flexible healthcare system.
Enhancing Interoperability and Coordination of Care
Interoperability can significantly enhance telehealth by ensuring coordination between telehealth platforms and other healthcare systems, such as in-person providers, clinics, and hospitals. Developing interoperability standards helps telehealth solutions share data consistently, such as complying with the HL7 standard. For example, telehealth platforms should integrate seamlessly with electronic health records (EHRs) from other providers. Improved interoperability also ensures that new telehealth platforms work well with existing healthcare technologies. This allows care providers to access a patient’s complete digital care record, benefiting the continuity and quality of care.
Conclusion
Telehealth has greatly improved patient safety and increased access to healthcare services. It provides opportunities for telemedicine, remote monitoring, and data integration. To build on these benefits, the country should continue investing in telehealth technologies and infrastructure. The future of telehealth will be vital for American healthcare, ensuring that everyone has access to high-quality care.
